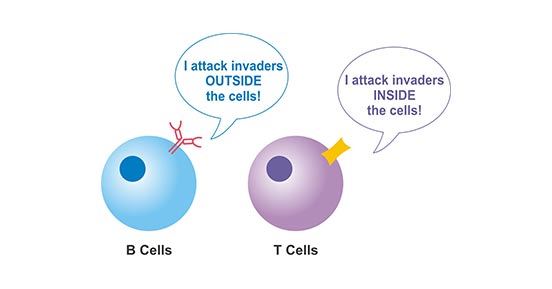
T Cells
Definition
T cells are a type of white blood cell that play an important role in the immune system.
Origin
T cells are produced in the bone marrow and mature in the thymus gland.
Functions
T cells are responsible for recognizing and destroying cells that have been infected with a virus, as well as cancer cells. There are several different types of T cells, including helper T cells, cytotoxic T cells, and memory T cells.
Types of T Cells
- Helper T cells are responsible for activating other immune cells, such as B cells and cytotoxic T cells.
- Cytotoxic T cells are responsible for directly attacking and destroying cells that have been infected with a virus or that are cancerous.
- Memory T cells are long-lived cells that are capable of recognizing and responding to a pathogen that the immune system has previously encountered.
B Cells
Definition
B cells are a type of white blood cell that play an important role in the immune system.
Origin
B cells are produced in the bone marrow.
Functions
B cells are responsible for producing antibodies that are specific to a particular pathogen. When a B cell encounters a pathogen, it produces antibodies that are specific to that pathogen. These antibodies then bind to the pathogen and mark it for destruction by other immune cells.
Types of B Cells
B cells also have the ability to develop into memory B cells, which are capable of producing antibodies in response to a pathogen that the immune system has previously encountered.
In conclusion, T cells and B cells are two types of white blood cells that play important roles in the immune system. T cells are responsible for recognizing and destroying cells that have been infected with a virus or that are cancerous, while B cells are responsible for producing antibodies that are specific to a particular pathogen.