Solute, solution, solvent, hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic are terms used to describe the properties of solutions in both chemistry and biology. Understanding these terms is essential for understanding how solutions behave and interact with living organisms.
Solute
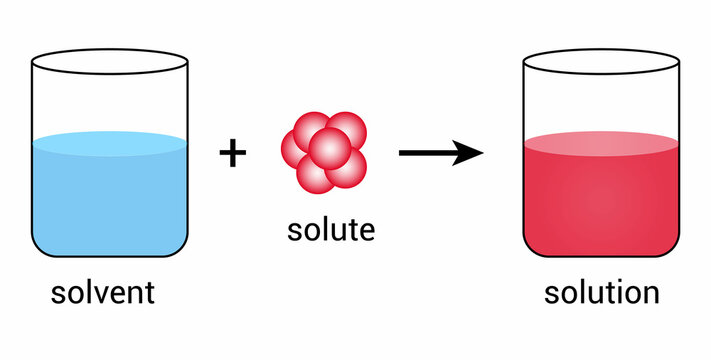
A solute is a substance that is dissolved in a solvent to form a solution. The solute is the substance that is present in a smaller amount in the solution. In chemistry, solutes are typically solids, but they can also be gases or liquids. In biology, solutes can be any substance that is dissolved in a solvent. For example, in saltwater, salt is the solute.
Solution
A solution is a homogeneous mixture of a solute and a solvent. A homogeneous mixture is one in which the components are evenly distributed throughout the mixture. Solutions can be solid, liquid, or gas. In chemistry, solutions are classified based on the physical state of the solute and solvent. For example, a solid solution is formed when a solid solute is dissolved in a solid solvent, and a gas solution is formed when a gas solute is dissolved in a gas solvent.
Solvent
A solvent is a substance that dissolves a solute to form a solution. The solvent is the substance that is present in a larger amount in the solution. In chemistry, solvents are typically liquids, but they can also be gases. In biology, water is the most common solvent. For example, in saltwater, water is the solvent.
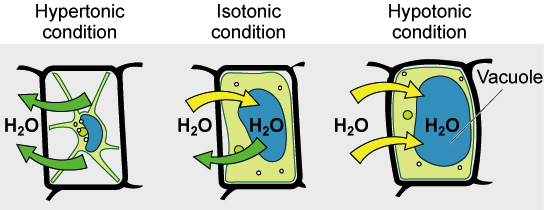
Hypertonic
A hypertonic solution is a solution that has a higher concentration of solutes than another solution. When a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, water will move out of the cell, causing the cell to shrink. Hypertonic solutions are used in medicine to treat edema, which is the swelling of body tissue due to excess fluid. For example, a hypertonic saline solution can be used to reduce swelling in the brain caused by head injuries.
Hypotonic
A hypotonic solution is a solution that has a lower concentration of solutes than another solution. When a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, water will move into the cell, causing the cell to swell. Hypotonic solutions are used in medicine to treat dehydration, which is the loss of body fluids. For example, a hypotonic saline solution can be used to rehydrate a person who has lost fluids due to vomiting or diarrhea.
Isotonic
An isotonic solution is a solution that has the same concentration of solutes as another solution. When a cell is placed in an isotonic solution, there is no net movement of water into or out of the cell, and the cell remains the same size. Isotonic solutions are used in medicine to replace lost fluids and electrolytes. For example, an isotonic saline solution can be used to treat dehydration caused by excessive sweating.
Conclusion
Solute, solution, solvent, hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic are important terms used to describe the properties of solutions in both chemistry and biology. Understanding these terms is essential for understanding how solutions behave and interact with living organisms.