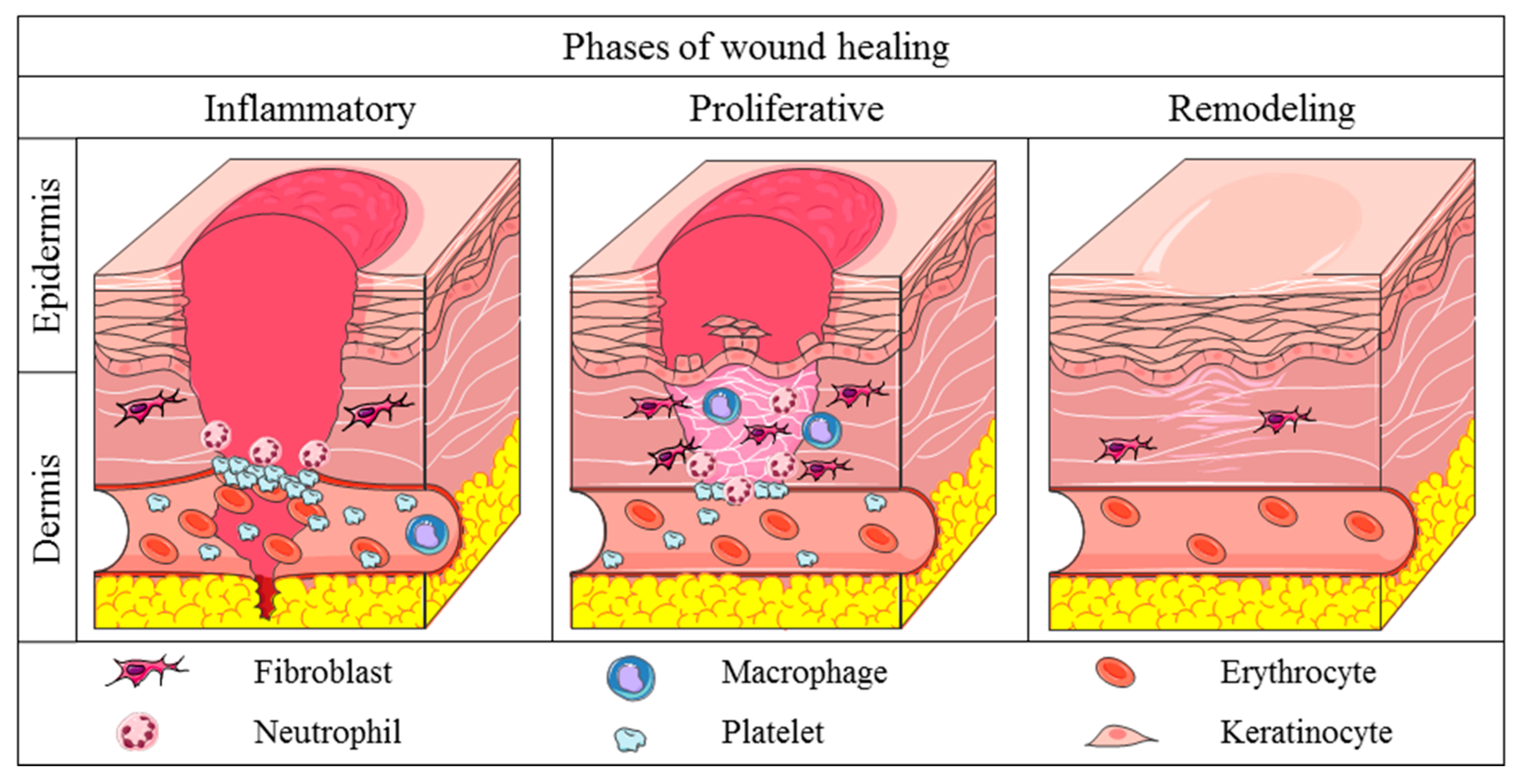
Wound healing consists of filling the gap that is caused by injury and tissue destruction, followed by the restoration of tissue continuity through the three phases:
- Inflammatory phase
- Proliferative phase
- Remodeling phase
Starting with the inflammatory phase: the purpose of this phase is to remove the injurious agents as well as preparing the wound for healing. So, when we see an injury, let's say you prick yourself with a thorn and there's tissue destruction in your skin. We have a whole lot of tissue that is damaged and as well as a blood vessel that is ruptured. Therefore, the wound would fill with blood and this is this first part of the inflammatory phase, known as hemostasis.
Hemostasis is a blood clot formation. This blood clot and ultimately the scab at the top would seal off the wound and allow the area to be closed.
The next part of the inflammatory phase is acute inflammation. This is where the blood vessel would dilate and bring more cells into the area that the wound would become hot and swollen and red. White blood cells would come into the area such as neutrophils and macrophages. These cells would phagocytize any dead cells as well as any microorganisms.
Therefore, allow the next phase to start which is the proliferative phase: The proliferative phase is where granular tissue is formed. This is caused by fibroblasts that come into the area the and that encourages new blood vessels to grow into the area that brings oxygen and nutrients. The growth factors from the fibroblasts will also cause new epithelial cells to start to form around the wound edge retract and finally the fibroblasts would lay down new collagen and extracellular matric. Matrix which gives a good scaffold for new tissue to form.
Finally moving to the remodeling phase: This begins three weeks after the initial injury, that granular tissue starts to become more scar tissue. This scar tissue becomes avascular, which means it loses its blood supply. This collagen will start to retract and then finally the scar will fade away in time and the tissue will go back to its original form.