If you have recently been treated for a heart attack a condition caused by a blockage of blood flow to your heart muscle. Then read this article carefully to understand the condition and its treatment.
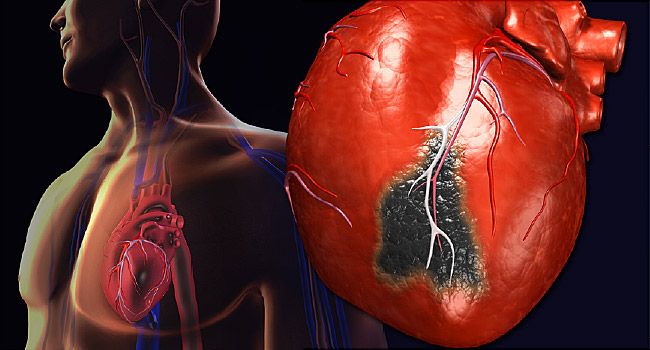
Your heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood containing the oxygen and nutrients your body needs. The main pumping chamber of your heart is the left ventricle. When your left ventricle contracts, it sends oxygen-rich blood to your body through a large artery called the aorta. Connected to your aorta our small arteries called coronary arteries.
Blood flows from your aorta through the coronary arteries to supply your heart muscle with oxygen and nutrients. During your heart attack blood flow through one of your coronary arteries, may have been severely reduced or completely blocked. Your reduced blood flow may have been caused by a buildup of a fatty substance called plaque in your coronary arteries. If this plaque became disrupted, a blood clot might form and severely worsen the narrowing or lead to a sudden complete blockage.
Stopping blood flow down the artery a blockage in your coronary arteries prevented the oxygen and nutrients in your blood from reaching that part of your heart supplied by the artery. As a result, heart muscle in that area started to die. Damage to part of your heart muscle is called a heart attack. It's also known as a myocardial infarction or MI.
Your heart doctor may have recommended a procedure to help open the blockage and improve blood flow to the damaged area. The procedure you had may have been a coronary angioplasty. During a coronary angioplasty a balloon tipped catheter inflates inside your blocked coronary artery to open it. The procedure may have involved placing a stent to help prop the artery open. This is usually a thin metal mesh that acts as a scaffold. Or you may have had a coronary artery, bypass graft or CABG.
CABG is a surgical procedure in which the blocked areas of the coronary arteries are by-passed with veins or other arteries from the body. Before you left the hospital, your healthcare provider most likely prescribed several medications.
Your medication may include the following:
Oral antiplatelet therapy: Helps prevent platelets from sticking together and forming new blood clots.
You may have also received drugs called beta blockers that help lower your heart rate and blood pressure.
Drugs such as angiotensin converting enzyme or ACE inhibitors: angiotensin receptor blockers or ARBs and calcium channel blockers also work to lower your blood pressure, if needed. And you may have been prescribed statins along with a low-fat diet to lower your cholesterol.
These drugs work by reducing the amount of cholesterol made in your liver. It is important to stay on your medications as your physician prescribed even if you are feeling better. Do not go off your medication unless the healthcare professional that prescribed them tells you to.